
|
CHINA> Official Publication
 |
|
Full text of white paper on ethnic policy
(china.org.cn)
Updated: 2009-09-27 17:05 V. Accelerating the Economic and Social Development of the Ethnic Minorities and Minority Areas Adhering to common prosperity and development of all ethnic groups is the fundamental stance of China's ethnic policy. The Constitution stipulates, "The state does its utmost to promote the common prosperity of all ethnic groups in the country." The Law on Regional Ethnic Autonomy stipulates that it is a legal obligation of the higher-level state organs to help the minority areas accelerate their development. Over the years, the state has made it a major part of national development to promote the economic and social progress of the ethnic minorities and minority areas, and has worked out from time to time policies and measures to this end. Before the founding of New China in 1949, most minority areas had an extremely low level of productivity, backward economic and social development, and extremely poor infrastructure. There was not an inch of railway in Xinjiang, not a single highway in Tibet, and in mountainous Yunnan, horses, elephants and suspension cables were all the locals could rely on for traveling or carrying goods. People of the ethnic minorities engaged mainly in traditional agriculture and animal husbandry. Some places were still in the primitive "slash-and-burn" state. In some areas, people still used wooden and stone tools; and iron tools were not yet widespread. The ethnic minorities led a life full of misery. Life was even worse for those living in the mountainous and desert areas, where a dearth of food and clothing was common. For months almost every year they would run out of grain and had to survive on wild fruits, and in the harsh winter they had nothing to keep out the cold but straw capes. All this hindered the progress of the ethnic minorities. Some of them were on the verge of extinction, with the Hezhen numbering only some 300 people at the time of the founding of New China. It was on such an extremely backward basis that the social and economic construction of the ethnic minorities and minority areas began in New China. The CPC and the central government have always supported the development of the ethnic minorities and minority areas. When New China was established, the Chinese government made it a basic task to rid all ethnic groups of poverty and enable them to lead a better life. Since the adoption of the reform and opening-up policies in the late 1970s, the state has focused on economic construction, given top priority to development, made increasing efforts and carried out several significant measures to quicken the advance of the ethnic minorities and minority areas. Over the years, the ethnic minorities and minority areas have all along upheld the spirit of self-reliance and hard working, coupled with assistance from economically advanced parts of China and state preferential policies, striven to build better homes for themselves. Thanks to the concerted efforts of the entire nation, the ethnic minorities and minority areas have seen one leap forward after another in their economic and social progress, completely got rid of stark poverty and backwardness, and entered a stage unparalleled in history. Priority given to construction projects to consolidate the foundation for further development In the early days of New China, the state gave top priority to infrastructure construction in the minority areas. In 1952 the central government issued the Principles of the Five-year Construction Plan for the Minority Areas, involving the construction of rails and trunk roads, the repair of existing roads and bridges, and the building of postal, telegraph, telephone and other communication systems in some minority areas. During China's First Five-year Plan period (1953-1957), the state started the construction of eight trunk railways, five of which, including the Lanzhou-Urumqi and Baotou-Lanzhou lines, were in minority areas or linked them with other places. In 1954 the two world-renowned highways connecting Tibet with Sichuan and Qinghai were completed. In the 1960s more railways were built, including the Chengdu-Kunming, Changsha-Guiyang and Panzhihua-Liuzhou lines, and the Yunnan-Tibet highway was also completed. In 1962 the Lan-zhou-Urumqi railway line, the first railway line in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, reached Urumqi. Since the late 1970s a large number of key projects have been completed in the minority areas, including the Nanning-Kunming, Neijiang-Kunming and Southern Xin-jiang railway lines, Lhasa Airport, the Lanzhou-Xining-Lhasa optical cable, and the project for utilizing water from the Yellow River for irrigation in Ningxia, which have greatly improved the transport and communication conditions and the livelihood in those minority areas. The state has made the development of local advantageous resources and modern industry a major measure to promote the advance of the ethnic minorities and minority areas. During the First Five-year Plan period, 40 of the 156 large state construction projects were initiated in the minority areas, such as the Baotou iron and steel base in Inner Mongolia, the Karamay oilfield in Xinjiang and the Gejiu tin company in Yunnan. In the 1960s the state moved a host of large industrial enterprises from coastal areas and inland places to the minority areas, thus laying the foundation for modern industry in the latter. Since the introduction of the reform and opening-up policies, the state again has approved a large number of massive projects in the minority areas, such as the Tarim oilfield in Xinjiang, the aluminum plant in Pingguo, Guangxi, the potash fertilizer plant in Qinghai and the coal and electric power base in Inner Mongolia, leading to the formation of several important industrial bases for resources development and processing in these minority areas, and blazing a trail for industrialization based on local resources and with local characteristics. Chart 3 Growth of Industrial Output Value in the Minority Areas
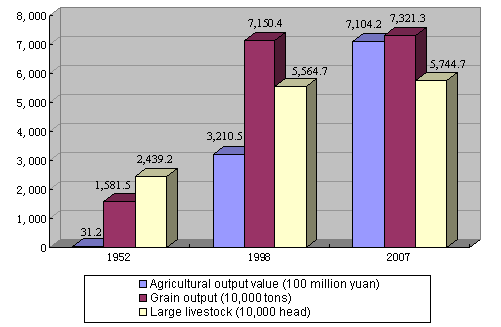
 Since 2000, when China introduced the strategy of large-scale development of its western regions, the state has made it a top task to accelerate the development of the ethnic minorities and minority areas. To ensure that they get tangible benefits, the state has adopted many preferential measures, such as giving priority to these areas when arranging resources development and processing projects, giving compensation to minority places that export natural resources, guiding and encouraging enterprises from economically advanced areas to invest in these places, and increasing financial input and support to them, so as to enhance their economic strength. At present, all of China's five autonomous regions, 30 autonomous prefectures and 120 autonomous counties nationwide are either covered by the "Develop the West" campaign, or enjoy the same preferential policies as the western regions. Chart 4 Agriculture and Animal Husbandry in the Minority Areas
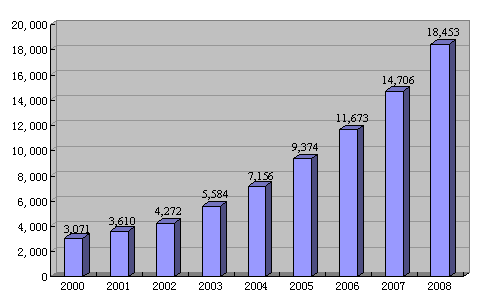
 The "Develop the West" campaign has brought about visible profits to the minority areas. By 2008 the accumulated fixed assets investment in these areas amounted to 7,789.9 billion yuan. Of that, 1,845.3 billion yuan was invested in 2008, which was five times that in 2000 and a rise of 23.7 percent on an annual basis. Key projects for transmitting gas and power from the west to the east have been completed, and a number of infrastructure projects, such as airports, expressways and water conservancy hubs, have been built. In 2007 the Qinghai-Tibet Railway was extended to Lhasa, giving a rail connection to Tibet for the first time in its history. A rapid, economical, all-weather transport channel of massive capacity between Tibet and the outside world, the railway has fundamentally changed the backward transport situation in the region, and added wings to the impending economic take-off of Tibet. Chart 5 Fixed Assets Investment in the Minority Areas Since 1999
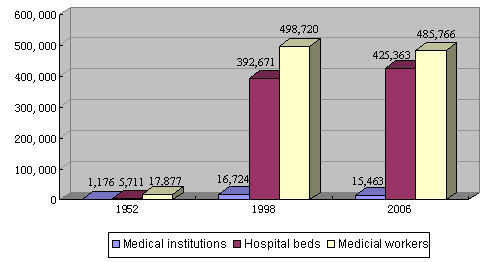
 The central government requires that when planning infrastructure projects located in the minority areas the local government either be exempted from contributing capital or contribute less; when developing resources or building enterprises in these areas, due consideration be given to local interests and the production and life of the ethnic minorities; and appropriate compensation be granted to places exporting natural resources or doing their bit for the eco-balance and environmental conservation. In 1994 the state adjusted the ratio between the amount of capital from the central budget and that from autonomous region governments to 6:4, while the ratio between the central government and the government of other provinces was fixed at 5:5. In 2004 the state adopted the compensation mechanism for ecological construction and environment protection. When tapping the rich oil and gas resources in Xinjiang, attention is paid to the stimulation effect on local development. The West-East Gas Transmission project alone can bring in over one billion yuan of revenue to Xinjiang a year. Poverty being the key issue to tackle to ensure and improve the well-being of the people Over the years, the state has adopted a series of policies and measures to relieve the poverty the ethnic minorities suffer. In the 1950s, the state provided free medical services to poor people of the ethnic minorities, granted them loans and farming tools, helped them set up schools and conducted social relief. In 1983, the State Council held a national meeting on production and livelihood in the minority areas, which decided to basically solve the problems of food and clothing, housing and drinking water within a short time. Since 1990 the state has set up a fund to assure the basic needs of people living in poverty-stricken minority areas, and 141 impoverished counties were listed as the first batch to gain this support. In 1994 the Seven-year Poverty Alleviation Program (a program designated to lift 80 million people out of absolute poverty in the seven years 1994-2000) was carried out, and, with the assistance threshold lowered, 116 more poverty-stricken minority counties were covered by state preferential policies. In 2001 the Outline of Rural Poverty-relief Development was implemented, with ten more minority counties included, and Tibet as special region covered. In 2005 the comprehensive development of poor minority villages became the focus of national poverty-relief efforts. In 2007 the state formulated the 11th Five-year Plan for the Development of the Ethnic Minorities, containing 11 key projects. In 2009 the state announced new standards for poverty-relief work, and expanded the coverage to low-income rural people in the minority areas. Other efforts include: providing work as a form of relief, relocating people from places with poor conditions, building settlements for formerly nomadic people, repairing dangerous housing for rural residents, supplying safe drinking water in rural areas, and providing minimum living allowances to rural and urban residents. Thanks to continuous efforts in these endeavors, the impoverished population in the minority areas shrank from some 40 million in 1985 to 7.7 million in 2008. Because of differences in history, culture, customs and religion, some ethnic minorities have special needs. For instance, the Tibetan, Mongolian, Uyghur and Kazak herdsmen need saddles, riding boots and brick tea, and the Muslims have their own special needs for Halal foods. To show respect for minority cultures and satisfy these special needs, the state has worked out preferential policies for the production of and trade in these items. In 1963 the state introduced preferential policies for ethnic-minority enterprises regarding profit retention, self-owned funds and price subsidies. In 1997 it enacted new preferential policies, set up special loans with discounted interest and exempted some enterprises from paying added value tax, benefiting 1,760 designated producers of special commodities needed by the ethnic minorities. In 1991 a mechanism for national brick-tea reserves was established to guarantee the supply of brick tea. In 2007 the state established a fund to ensure the production and promotion of the special commodities needed by the ethnic minorities, as well as related personnel training. Priority is also given by the state to improving medical and health care for the ethnic minorities and in the minority areas. The level of medical services in minority urban areas has been remarkably enhanced, the medical conditions in agricultural and pastoral areas have been noticeably improved, the difficulty of the ethnic minorities in getting adequate medical service has been alleviated, and the health of the ethnic minorities been improved considerably. Since the introduction of the reform and opening-up policies, the state has built or renovated township hospitals, and county-level epidemic-prevention stations and health centers for women and children, thus greatly improving the health-care services in the minority areas. More than 80 percent of the counties in Tibet now have epidemic-prevention stations. The state is making continuous efforts to prevent and treat endemic and epidemic diseases in the minority areas, and the once-prevalent Keshan disease, tuberculosis and Kaschin-Beck disease have been basically put under control. Through various channels, the state has trained health care workers for the ethnic minorities, and expanded the contingent of medical professionals. In Xinjiang one third of all medical workers are from ethnic minorities. Chart 6 Improvement of Medical Services in the Minority Areas
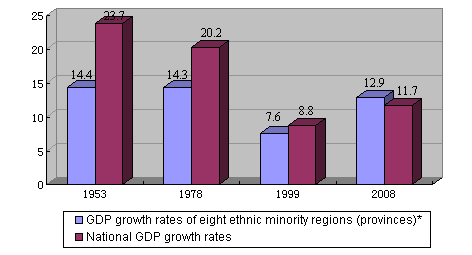
 Vigorous support for the pasturelands and borderlands for balanced development China's major pasturelands are all located in areas inhabited by the ethnic minorities, and animal husbandry has been the basic industry for most or part of the Mongolians, Tibetans, Kazaks and a dozen other ethnic minorities since ancient times. Since 1953 a milder taxation policy than in cities and farming areas has been enforced in the pasturelands, in addition to policies encouraging pasture protection and the settlement of nomadic people. After China began its reform and opening-up, the state adopted policies that allowed households to own livestock and contract pastures for independent operation. At a national work conference for pastoral areas held in 1987 the State Council listed 27 poverty-stricken pastureland counties as eligible for state assistance, and granted poverty-relief loans with discounted interest to support the pasturelands. To ensure the balanced development of animal husbandry and agriculture, in 1999 the Chinese government stressed that equal emphasis should be placed on grassland construction and farmland capital construction. In 2005 the state abolished taxes on agriculture and animal husbandry. After decades of unremitting endeavors, the minority areas have grown into important production bases of agricultural and animal products. Inner Mongolia now produces one fifth of the nation's total milk, ranking first in China in milk production, and Xinjiang is the country's second-biggest producer of wool and cashmere. Most of China's borderlands are inhabited by ethnic minorities. In 1979 the state worked out the Borderlands Construction Plan (Draft), allocating 40 billion yuan for the construction of these areas over eight years. In 1992 China implemented its frontier opening-up strategy, designating 13 open cities and 241 first-grade open ports, and establishing 14 border economic and technological cooperation zones. In 1996 the State Council worked out preferential policies for promoting border trade and economic cooperation with other countries. In 1999 the state initiated a program to boost the borderlands' economy and help the local residents raise their incomes. This was followed by the formulation and execution of the 11th Five-year Plan for the Economic Development of the Borderlands, starting in 2005. In 2009 the government decided to expand the program to all frontier counties and the frontier farms under the Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps. So far, the central government has invested 1.446 billion yuan and built more than 20,000 projects in the borderlands. For decades the state has paid steady attention to the construction and protection of ecological environment in the minority areas. Especially since the launch of the "Develop the West" campaign, a series of policies and measures have been executed, including prohibiting tree felling on the upper reaches of major rivers, returning farmlands to forests and grasslands and closing hillsides for afforestation. As compensation, the state has distributed grain to farmers and herdsmen to make up for their losses in returning their farmlands to forests or grasslands, and subsidies to places where revenue has shrunk because of the restriction on tree felling. In recent years, the Chinese government has increased its support for the sparsely-populated minority areas with poor conditions. In 2005 it formulated and implemented the Program to Support the Ethnic Minorities with Small Populations (2005-2010), and listed 640 ethnic-minority villages as recipients of assistance. So far, 1.253 billion yuan has been forthcoming for these areas from the central government. Constantly increasing financial support and actively organizing paired-up assistance Over the past 60 years both the central and local governments at all levels have gradually increased their efforts to extend fiscal transfer payments to the minority areas. In the 1950s the state began to implement preferential fiscal policies for these areas, such as "unified collection of revenues and allocation of expenditures and subsidies for the needy," and raising the proportion of the financial reserve fund (two percentage points higher than in other regions). From 1980 to 1988 the central financial authorities adopted a quota subsidy system with a yearly increase of ten percent for the five autonomous regions and the three provinces with large ethnic-minority populations — Guizhou, Yunnan and Qinghai. In 1994 the state began to adopt a tax-sharing system, and introduced the system of policy-related transfer payments to the minority areas. In 2000 China initiated transfer payments for the minority areas on top of the general transfer payments and special-fund transfer payments as prescribed by relevant regulations. From 1978 to 2008 the total transfer payments by the central financial authorities to the minority areas totaled 2,088.94 billion yuan, with an annual increase of 15.6 percent. In 2008 alone the amount was 425.3 billion yuan, making up 23.8 percent of the nation's total transfer payments. According to incomplete statistics, from 1959, when democratic reform began in Tibet, to 2008, fiscal assistance from the central budget to Tibet reached 201.9 billion yuan, with an annual increase of nearly 12 percent; from 1955, when the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region was established, to 2008, the fiscal assistance from the central budget to Xinjiang reached 375.202 billion yuan, with an annual increase of 11 percent, the sum in 2008 being 68.56 billion yuan. In addition, the state has also set up a variety of special funds to help resolve the difficulties encountered by the minority areas and accelerate their development, including education development subsidies for the ethnic minorities set up in 1951, minority area subsidies set up in 1955, the minority-area reserve fund set up in 1964, subsidy for border construction set up in 1977, fund for aiding economically underdeveloped areas set up in 1980, and fund for the development of the ethnic minorities set up in 1992. The state vigorously organizes and encourages paired-up assistance between the economically developed areas and the less-developed minority areas. In 1979 it decided to pair up such areas, for example, getting Beijing to assist Inner Mongolia, Hebei to assist Guizhou, Jiangsu to assist Guangxi and Xinjiang, Shandong to assist Qinghai, Shanghai to assist Yunnan and Ningxia, and the whole nation to assist Tibet. In 1996 the State Council determined to organize the 15 developed provinces and cities along the eastern coast to provide aid to 11 western provinces (autonomous regions and municipality directly under the central government), and mobilized all departments of the central government to provide pair-up aid to the impoverished areas. In order to promote the development of Tibet, the central government has held four forums on work in that region. Since 1994 the state has arranged more than 60 central government departments, 18 provinces (municipalities directly under the central government) and 17 state-owned enterprises to provide paired-up aid to various places in Tibet. By the end of 2008, a total of 6,050 assistance projects had been launched in Tibet, with a total of 11.128 billion yuan in assistance money. In recent years the state has further strengthened its efforts to aid the ethnic minorities and minority areas under the guidance of the Scientific Outlook on Development. In 2005 the CPC Central Committee and the State Council jointly issued the Decision on Further Strengthening the Work on the Ethnic Minorities and Promoting Social and Economic Development in the Minority Areas, which stipulated that development is the key to overcoming difficulties and solving problems in the minority areas, and stressed that, with the gradual increase of the country's comprehensive strength, the central government would continuously strengthen support to the ethnic minorities and minority areas in their social and economic development, improve the policy-related transfer payment system compatible with the system of regional ethnic autonomy, help the minority areas build infrastructure projects that will give an impetus to local social and economic development and give special treatment to small and medium-sized public welfare projects that are closely related to the everyday life of local people. In 2007 the State Council released Some Opinions on Further Promoting Social and Economic Development in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, which contained requirements and plans to accelerate the social and economic development of Xinjiang and further improve the living standards of the people of all ethnic groups there. Since 2008 the state has drawn up and issued a series of preferential policies to promote the social and economic development of the Tibetan-inhabited areas in Ningxia and Qinghai and the border areas of Yunnan, increasing input to strengthen the building of infrastructure, develop competitive industry, push forward the development of social undertakings and accelerate the social and economic development of the minority areas there. Under the central leadership and with the full support of the whole nation and the strenuous efforts made by the people of all ethnic groups in the minority areas, great achievements in social and economic development have been scored in the minority areas, and people's living standards there have markedly improved. In 2008 the economic aggregate of the minority areas reached 3,062.62 billion yuan, from 5.79 billion yuan in 1952, an increase of 92.5 times calculated at comparable prices. The urban per-capita disposable income increased to 13,170 yuan from 307 yuan in 1978, an increase of over 30 times; and the per-capita net income of farmers and herdsmen came to 3,389 yuan from 138 yuan in 1978, an increase of 19 times. The economic growth rate of Inner Mongolia has ranked top in the country for seven consecutive years, and Xinjiang has maintained double-digit growth for six years in succession. In the same year, the GDP of Tibet stood at 39.591 billion yuan, an increase of 65 times compared with 1959. The rapid economic and social development in the minority areas has laid a solid foundation for the prosperity of all ethnic groups. According to the national census of 2000, the average life expectancy of 13 ethnic minorities was above the average national level of 71.40 years, and seven above the average Han level of 73.34 years. The population of the Hezhe ethnic group has increased from 300 in the early days of New China to over 4,000. Xinjiang is listed by the International Medical Union as one of the four regions in the world renowned for longevity, with the biggest number of people over 100 years among every million people in the country. The average life expectancy of Tibet has increased from 35.5 years in 1951, when it was peacefully liberated, to 67 years now, with 13,581 seniors aged from 80 to 99, and 62 seniors aged over 100; it is now among the regions with the most centenarians on average in China. Chart 7 A Comparison of GDP Growth Rates of Eight Ethnic Minority Regions (Provinces) with National GDP Growth Rates
*Note: The eight autonomous regions and provinces where ethnic minorities live in compact communities are: Inner Mongolia, Xinjiang, Guangxi, Ningxia and Tibet autonomous regions, and Guizhou, Yunnan and Qinghai provinces. Chart 8 GDP and Fiscal Revenue of the Minority Areas
 |
主站蜘蛛池模板: 宝鸡市机械有限公司| 温岭联星机械有限公司| 西安飞鸿机械有限公司| 江苏正合重工有限公司| 纸箱机械制造有限公司| 中山凌宇机械有限公司| 范斯特机械有限公司| 东莞市通机械有限公司| 阿特拉斯工程机械有限公司| 苏州松博机械有限公司| 深圳市鑫台铭机械设备有限公司| 丽驰精密机械有限公司| 上海起思宠物有限公司| 青岛海佳机械有限公司| 江苏谷登工程机械装备有限公司| 金泰机械制造有限公司| 常州安捷起重吊装有限公司| 捷赛机械苏州有限公司| 济南耐刻机械设备有限公司| 苏州纺织机械有限公司| 上海松精机械制造有限公司 | 大连华威机械有限公司| 五矿钢铁西安有限公司| 东莞市联顺机械有限公司| 河南新起点印务有限公司| 唐山众达机械轧辊有限公司| 常州天山重工机械有限公司| 杭州引春机械有限公司| 阳春市新钢铁有限公司| 山东机械制造有限公司| 福建三联机械有限公司| 无锡南机械有限公司| 邯郸新兴重型机械有限公司| 上海杰姆博机械设备有限公司| 三马起重机有限公司| 常州市佳凯包装机械有限公司| 沈阳华扬机械有限公司| 郑州市天赐重工机械有限公司| 济南液压机械有限公司| 上海轶鹰起重机械有限公司| 京西重工北京有限公司| 鼎泰盛机械有限公司| 安徽中科光电色选机械有限公司| 江苏华夏重工有限公司| 山东天龙机械有限公司| 上海中远海运重工有限公司| 无锡布勒机械有限公司| 深圳龙润彩印机械设备有限公司 | 泰田机械制造有限公司| 瑞安正博机械有限公司| 盐城丰炜机械制造有限公司| 江苏利淮钢铁有限公司| 唐山神州机械有限公司| 上海金纬挤出机械制造有限公司| 上海竹达机械设备有限公司 | 宁波甬龙机械有限公司| 东莞市台克机械有限公司 | 河南省力神机械有限公司| 江苏宏程重工有限公司| 浙江赛峰机械有限公司| 玉环华邦机械有限公司| 青岛 机械有限公司| 新疆昆仑钢铁有限公司| 德龙钢铁有限公司地址| 速技能机械有限公司| 河南良益机械有限公司| 天津起重机械有限公司| 浙江制药机械有限公司| 中核华兴达丰机械工程有限公司| 徐工基础工程机械有限公司| 沈阳韩兆机械有限公司| 中山弘立机械有限公司| 苏州伟鼎机械设备有限公司| 浙江江鑫机械有限公司| 江阴铸造机械有限公司| 无锡金球机械有限公司| 恩比尔(厦门)机械制造有限公司| 广濑精密机械有限公司| 卡麦龙机械有限公司| 河北圣禹水工机械有限公司| 东莞市世翔精密机械制造有限公司 | 乐清市机械有限公司| 上海敏硕机械配件有限公司| 德昌机械制造有限公司| 扬州冶金机械有限公司| 永盛机械设备有限公司| 山东金成机械有限公司| 三友重工机械有限公司| 辽宁春光机械有限公司| 山东正阳机械有限公司| 广州振通机械有限公司| 洛阳中冶重工机械有限公司| 通达塑料机械有限公司| 浙江新飞机械有限公司| 抚顺起亮食品有限公司| 济南盛润机械有限公司| 江苏船谷重工有限公司| 河南重型机械有限公司| 中泰机械设备有限公司| 蓬莱万寿机械有限公司| 临沂华星机械有限公司| 上海景林包装机械有限公司| 贵阳闽达钢铁有限公司| 新疆八一钢铁有限公司| 河南省起重机有限公司| 厦门精密机械有限公司| 济南恒铭钢铁有限公司| 洛阳友建工程机械有限公司| 上海申虎包装机械设备有限公司| 上海颖盛机械有限公司| 东阳机械制造有限公司| 广东长征机械有限公司| 中山力劲机械有限公司| 石家庄食品机械有限公司| 精密机械电子有限公司| 万利达机械铸造有限公司| 成都机械设备有限公司| 永洋钢铁有限公司电话| 深圳市铭利达精密机械有限公司| 杭州九钻机械有限公司| 江西四通重工机械有限公司| 四川阳光机械有限公司| 上海固好包装机械有限公司| 广州市 工程机械有限公司| 瑞 机械有限公司| 新乡市西贝机械有限公司| 山东力王重工机械有限公司| 苏州孚杰机械有限公司| 东莞鸿铭机械有限公司| 东莞正扬电子机械有限公司| 上海捷如重工机电设备有限公司| 无锡聚英机械有限公司| 浙江吉隆机械有限公司| 山东米科思机械设备有限公司| 中海福陆重工有限公司| 吉林鑫达钢铁有限公司地址 | 晋江机械制造有限公司| 广州泽比机械设备有限公司| 益丰泰机械有限公司| 杭州丽伟电脑机械有限公司| 昆山海进机械有限公司| 山东金大丰机械有限公司| 宝鸡 机械有限公司| 广州坚诺机械设备有限公司 | 瑞安市包装机械有限公司| 洛阳泽华机械设备有限公司| 广州汉达机械有限公司| 常州亚美柯机械设备有限公司| 广东韶关钢铁有限公司| 靖江机械制造有限公司| 四川华为钢铁有限公司| 力源液压机械有限公司| 苏州升降机械有限公司| 贝纳特机械有限公司| 潍坊圣川机械有限公司| 广州机械有限公司 v| 江阴市永昌药化机械有限公司| 宁波天佳塑料机械有限公司| 大华机械制造有限公司| 张家港市通惠化工机械有限公司| 荏原机械烟台有限公司| 上海包装机械设备有限公司| 永华机械有限公司招聘| 南通明德重工有限公司| 沈阳黎明机械有限公司| 无锡通用机械厂有限公司| 常州包装机械有限公司| 常州杰洋精密机械有限公司| 青岛广德机械有限公司| 玉环机械制造有限公司| 俊杰机械深圳有限公司| 深圳印刷机械深圳有限公司| 东莞市和明机械有限公司| 嘉厨食品机械有限公司| 鹤壁万丰矿山机械制造有限公司 | 机械自动化有限公司| 山西风源机械制造有限公司| 中信重工开诚智能装备有限公司| 东莞市台克机械有限公司| 昆山美和机械有限公司| 云南昆鼎机械设备有限公司| 邢台机械制造有限公司| 石嘴山钢铁有限公司| 首钢凯西钢铁有限公司| 郑州同鼎机械设备有限公司| 浙江启博机械有限公司| 上海钢铁物资有限公司| 南通中船机械制造有限公司| 徐州工程机械有限公司| 山东润通机械制造有限公司| 山东威力重工机床有限公司 | 绿友园林机械有限公司| 济南闽源钢铁有限公司| 张家口煤矿机械有限公司| 上海博强机械有限公司| 广东精密机械有限公司| 潍坊钰兴机械有限公司| 东莞住重塑胶机械有限公司| 成都瑞迪机械实业有限公司| 广州南头机械有限公司| 江苏鑫锋重工机床有限公司| 汉中燕航精工机械有限公司| 泰兴机械制造有限公司| 浙江恒齿传动机械有限公司| 沈阳机械制造有限公司| 杭州纺织机械有限公司| 西安科迅机械制造有限公司| 沈阳 机械制造有限公司| 上海精元机械有限公司| 南京赛达机械制造有限公司 | 上海德采包装机械有限公司| 浙江劲豹机械有限公司| 杭州科豪机械有限公司| 山东天力液压机械有限公司| 重庆机械租赁有限公司| 扬州冶金机械有限公司| 杭州力士机械有限公司| 天津江天重工有限公司| 农友机械设备有限公司| 上海 坚机械有限公司| 龙海起重工具有限公司| 湖南金塔机械制造有限公司| 禹城 机械 有限公司| 南通太和机械有限公司| 无锡英那威特机械发展有限公司| 云南德胜钢铁有限公司| 南京机械设备有限公司| 金鹰重型工程机械有限公司| 上海烨昌食品机械有限公司| 青岛日川精密机械有限公司| 西安 机械设备有限公司| 石家庄机械有限公司| 福建海源机械有限公司| 杭州天杨机械有限公司| 柳州富达机械有限公司官网| 建湖县液压机械有限公司| 业精机械制造有限公司| 东莞宝科机械有限公司| 中山弘立机械有限公司| 张家口中煤嘉益机械制造有限公司 | 浙江云广机械制造有限公司| 东莞市途锐机械有限公司| 哈尔滨机械制造有限公司| 广东力源液压机械有限公司| 佛山市宝索机械制造有限公司| 山东海宏重工有限公司| 徐州斗山工程机械有限公司| 温州市顺达服装机械有限公司| 河北圣和农业机械有限公司| 上海中吉机械有限公司| 杭州速能机械有限公司| 无锡速波精密机械有限公司| 兖州丰业机械有限公司| 安宁市永昌钢铁有限公司| 济宁经纬工程机械有限公司| 天津瑞星传动机械有限公司| 东莞市利成机械有限公司| 中船重工环境工程有限公司怎么样 | 浙江齐鲤机械有限公司| 苏州擎邦机械有限公司| 湖州惠盛机械有限公司| 斗山工程机械苏州有限公司| 东莞市鼎祥通用机械设备有限公司| 重型机械制造有限公司| 固精密机械有限公司| 青岛大牧人机械有限公司| 宁波金记机械有限公司| 洛阳天宇机械制造有限公司| 万金机械配件有限公司| 杭州莱顿机械有限公司| 潍坊元鸣机械有限公司| 济南东泰机械制造有限公司| 河南省中原起重机械有限公司| 浙江荣众机械有限公司| 恒丰机械配件有限公司| 保定华光机械有限公司| 中意机械苏州有限公司| 苏州伟鼎机械设备有限公司| 顺德富华工程机械制造有限公司| 昆玉钢铁有限公司招聘| 武汉益达建设机械有限公司| 南阳鼎鑫钢铁有限公司| 中山市 机械有限公司| 合肥包装机械有限公司| 鞍山宝得钢铁有限公司| 常州久压久机械制造有限公司 | 沈阳凯力拓机械设备有限公司 | 青岛南牧机械设备有限公司 | 嘉兴 机械有限公司| 山东 工程机械有限公司| 丰精密机械有限公司| 东莞市世翔精密机械制造有限公司 | 牛力机械制造有限公司| 长沙市机械有限公司| 江苏别具匠心机械设备有限公司 | 镇江机械设备有限公司| 华隆 机械有限公司| 威海 机械有限公司| 佛山定中机械有限公司| 佛山市科鹰机械有限公司| 上海紫明印刷机械有限公司| 曲靖呈钢铁有限公司| 范斯特机械有限公司| 广东力源液压机械有限公司| 郑州食品机械有限公司| 中实洛阳重型机械有限公司实习报告 | 张家港市塑机械有限公司| 机械(上海)有限公司| 珠海康信精密机械有限公司| 丝网机械设备有限公司| 沁阳宏达钢铁有限公司| 连云港机械制造有限公司| 佛山液压机械有限公司| 西安凌通机械有限公司| 重庆宝汇跨搏机械制造有限公司 | 苏州精创机械有限公司| 江阴博纬机械有限公司| 北京洛克机械有限公司| 三一汽车起重机械有限公司| 长江液压机械有限公司| 洛阳美卓重工机械有限公司| 兴澄特种钢铁有限公司| 金华市机械有限公司| 昆山鑫建诚机械设备有限公司| 群基精密机械有限公司| 济南天业工程机械有限公司| 重庆辉昌机械设备有限公司| 陕西恒德精密机械有限公司| 上海卓亚矿山机械有限公司| 亿煤机械装备制造有限公司| 苏州德派机械有限公司| 唐山前进钢铁有限公司| 河南康迪机械有限公司| 武汉鑫金泽机械有限公司| 派克包装机械有限公司| 重庆华渝重工机电有限公司| 莱州三和机械有限公司| 宁波工程机械有限公司| 天津钢管钢铁贸易有限公司| 淄博捷达机械有限公司| 苏州毕特富精密机械有限公司 | 江苏天泽精工机械有限公司| 宁波星源机械有限公司| 苏州信能精密机械有限公司| 昆山富日精密机械有限公司| 上海一达机械有限公司| 山东润通机械制造有限公司| 张家港市机械有限公司| 东莞市嘉鲁特注塑机械有限公司 | 沈阳恒力机械有限公司| 泰田机械制造有限公司| 上海宝闽钢铁有限公司| 杭州天恒机械有限公司| 温州包装机械有限公司| 无锡名震机械制造有限公司| 福州 机械 有限公司| 扬州意得机械有限公司| 上海塑料机械 有限公司| 宁波昌源机械有限公司| 浙江金华机械有限公司| 浙江赛峰机械有限公司| 余姚市机械有限公司| 河南发达起重机有限公司| 精密机械配件有限公司| 上海鸿尔机械有限公司| 广州起重机械有限公司招聘| 铜陵市富鑫钢铁有限公司| 重庆春仁机械有限公司| 九江萍钢钢铁有限公司| 东莞市泽源机械有限公司| 南阳市 机械有限公司| 山东巨威机械有限公司| 深圳市康铖机械设备有限公司| 浙江临海机械有限公司| 济南龙铸液压机械有限公司| 深圳市精密达机械有限公司| 芜湖富鑫钢铁有限公司| 江阴江顺精密机械零部件有限公司| 京龙工程机械有限公司| 泰安越泰机械有限公司| 东莞%机械制造有限公司| 天津包装机械有限公司| 山东永峰钢铁有限公司| 武汉 机械有限公司| 鑫达机械制造有限公司| 长沙天映机械有限公司| 合肥汉杰包装机械喷码有限公司| 道依茨法尔机械有限公司| 东莞市乔锋机械有限公司| 张家港市旺巴巴机械有限公司| 鼎业机械设备有限公司| 上海德元机械设备有限公司| 东莞机械设备制造有限公司| 江苏国瑞液压机械有限公司 | 张市机械机械有限公司| 江苏汉鼎机械有限公司| 浙江鑫辉机械有限公司| 电子有限公司起名大全| 泉州泉盛机械有限公司| 上海纽荷兰农业机械有限公司| 江阴市华夏包装机械有限公司| 河南正亚机械设备制造有限公司| 莱州弘宇机械有限公司| 深圳华盛昌机械实业有限公司| 东莞安默琳机械制造技术有限公司 | 上海化工机械厂有限公司| 山东领品机械有限公司| 嘉善精密机械有限公司| 台州市双辉机械设备有限公司| 沈阳维用精密机械有限公司招聘| 杭州五金机械有限公司| 郑州水工机械有限公司| 东方液压机械有限公司| 徐州随车起重机有限公司| 江苏久盛机械设备有限公司| 湖南机械设备有限公司| 上海起重运输机械厂有限公司 | 河南 机械设备有限公司| 广东富华重工制造有限公司| 海狮洗涤机械有限公司| 太行机械工业有限公司| 浩强精密机械有限公司| 泉州明辉机械有限公司| 安徽泰源工程机械有限公司| 江阴机械制造有限公司怎么样 | 江源机械制造有限公司| 鑫港机械制造有限公司| 佛山市松川机械设备有限公司 | 天津泰威机械有限公司| 浙江起步儿童用品有限公司| 成都杰瑞达工程机械有限公司| 宁波市鸿博机械制造有限公司| 邹平 机械有限公司| 定州市机械有限公司| 南京康尼精密机械有限公司 | 铭诚机械制造有限公司| 山东 工程机械有限公司| 济南液压机械有限公司| 湛江市机械有限公司| 上海齐耀重工有限公司| 山西新泰钢铁有限公司| 杭州天扬机械有限公司| 郑州鼎盛机械设备有限公司| 中核华兴达丰机械工程有限公司| 山东神力起重机械有限公司| 上海达辉机械有限公司| 江苏苏东化工机械有限公司| 宁波华美达机械制造有限公司 | 台州欧玮机械有限公司| 宁波方力机械有限公司| 宝德机械国际有限公司| 潍坊大众机械有限公司| 江苏迪迈机械有限公司| 杭州精密机械有限公司| 陕西重型机械制造有限公司 | 南通友德机械有限公司| 江苏聚丰园林机械有限公司| 山东誉亚大豆机械制造有限公司 | 杭州纺织机械有限公司| 长城重型机械制造有限公司| 杭州精工机械有限公司| 宝鸡市机械有限公司| 上海瑞阳机械有限公司| 泰安通远机械有限公司| 吉林牧神机械有限公司| 上海航空机械有限公司| 河南龙昌机械制造有限公司| 临沂机械设备有限公司| 苏州海盛精密机械有限公司怎么样| 南通武藏精密机械有限公司招聘 | 成都精密机械有限公司| 南京儒一航空机械装备有限公司| 常州市昊博机械有限公司| 广州新麦机械有限公司| 邯郸新兴重型机械有限公司| 鼎业机械设备有限公司| 罗源闽光钢铁有限公司| 鑫阳机械设备有限公司| 江苏润山机械有限公司| 广东耐施特机械有限公司| 洛阳翼明机械有限公司| 承德建龙钢铁有限公司| 上海 机械 有限公司| 濮阳崛起装饰有限公司| 业精机械制造有限公司| 新疆机械设备有限公司| 湖南汇一制药机械有限公司| 杭州岛文机械有限公司| 浙江华球机械制造有限公司 | 青岛张氏机械有限公司| 普瑞特机械有限公司| 天津市天重江天重工有限公司| 凯斯纽荷兰机械 哈尔滨 有限公司| 泸州益鑫钢铁有限公司| 机械化工工程有限公司| 广州众起办公用品有限公司| 如皋市联创捏合机械有限公司 | 无锡传动机械有限公司| 烟台山一机械有限公司| 山东正阳机械有限公司| 云南德胜钢铁有限公司| 兰州华诚石化机械制造有限公司 | 潍坊华全动力机械有限公司| 咸阳 机械制造有限公司| 安徽省中冶重工机械有限公司| 华劲机械制造有限公司| 泰州机械 有限公司| 深圳巨涛机械设备有限公司| 河北展利机械有限公司| 泉州精镁机械有限公司| 庆达机械制造有限公司| 河南瑞峰机械有限公司| 湖南汇杰机械设备有限公司| 南京 机械有限公司| 宁波金记机械有限公司| 上海冠龙机械有限公司| 江阴鼎力起重机械有限公司| 江阴凯迈机械有限公司| 河南广泰机械有限公司| 浙江盾安机械有限公司| 张家口中煤嘉益机械制造有限公司| 河南万杰食品机械有限公司| 台州万州机械有限公司| 上海路桥机械有限公司| 上海钦典机械制造有限公司| 青岛日佳机械有限公司| 东莞市台钢机械设备有限公司| 佛山市康思达液压机械有限公司 | 亿煤机械装备制造有限公司 | 浙江 机械 有限公司| 华亿机械制造有限公司| 吉林鑫达钢铁有限公司| 巩义市瑞赛克机械设备有限公司| 天津机械设备有限公司| 沈阳维用精密机械有限公司招聘| 安徽富鑫钢铁有限公司| 青岛欣鑫数控精密机械有限公司| 德州机械制造有限公司| 银丰弹簧机械设备制造有限公司| 迁安九江钢铁有限公司| 沈阳六合机械有限公司| 河南宏基矿山机械有限公司| 苏州市大华精密机械有限公司| 张市机械机械有限公司| 江阴市华夏包装机械有限公司| 上海港机重工有限公司| 鑫成机械设备有限公司| 广州市 机械有限公司| 宏信机械设备有限公司| 湖北天腾重型机械制造有限公司| 新宝泰钢铁有限公司| 长沙宏银机械有限公司| 大华机械制造有限公司| 欧亚德机械有限公司| 无锡中机械有限公司| 上海杉野机械有限公司| 台州市鲨鱼食品机械有限公司| 南京康尼精密机械有限公司| 唐山市神州机械有限公司| 广州而众机械有限公司| 大连连美机械有限公司| 滦南华瑞钢铁有限公司| 长葛机械制造有限公司| 南通宝钢钢铁有限公司| 昆山苏隆机械制造有限公司| 莱州行星机械有限公司| 玉环县三和机械制造有限公司| 河南人从众机械制造有限公司| 西安海焱机械有限公司| 三友医疗机械有限公司| 新乡市东振机械制造有限公司| 沧州恒宇机械有限公司| 苏州恒威海绵机械有限公司| 郑州宇机械有限公司| 和本精密机械有限公司| 南通新兴机械制造有限公司| 温州 机械有限公司| 无锡起重机械有限公司| 江苏苏东化工机械有限公司| 武汉泛洲机械制造有限公司| 定州宏远机械有限公司| 友嘉精密机械有限公司| 上海亚遥工程机械有限公司| 宇进注塑机械有限公司| 东莞市联顺机械有限公司| 上海舒平精工机械有限公司| 昆山来运机械设备有限公司| 新乡市豫新起重机械有限公司| 江阴市机械有限公司| 斯特机械制造有限公司| 深圳电子机械有限公司| 无锡 液压机械有限公司| 扬州 液压机械有限公司| 宝 重工机械有限公司| 上海松铭传动机械有限公司| 江苏骏马压路机械有限公司| 开封元创机械有限公司| 济南捷迈数控机械有限公司| 海门亿峰机械有限公司| 山东鲁成起重机械有限公司| 建筑工程机械租聘有限公司 | 盐城中热机械有限公司| 安阳嘉和机械有限公司| 宁波德霖机械有限公司| 江西中天机械有限公司| 湛江恒润机械有限公司| 浙江超洋机械有限公司| 济南达润机械有限公司| 利勃海尔机械大连有限公司| 山东宏鑫机械有限公司| 绵阳科睿机械有限公司| 大阳通用机械有限公司| 杭州海特机械有限公司| 首钢长白机械有限公司| 宁波金记机械有限公司| 宁波民盛机械有限公司| 宁波敏达机械有限公司| 新能源有限公司起名| 华劲机械制造有限公司| 南方动力机械有限公司| 大牧人机械有限公司| 郑州永兴重工机械有限公司| 昆山海进机械有限公司| 淄博张钢钢铁有限公司| 浙江海工机械有限公司| 上海诚达机械有限公司| 山东兴源机械有限公司| 鞍山机械设备有限公司| 杭州 机械设备有限公司| 山东烨辉钢铁有限公司| 中山伙伴自动化机械有限公司| 潍坊元鸣机械有限公司| 河南丰泉机械有限公司| 上海宝日机械制造有限公司| 浙江吉隆机械有限公司| 上海航空机械有限公司| 长沙中京机械有限公司| 浙江康明斯机械有限公司| 常州包装机械有限公司| 陕西重型机械制造有限公司 | 安徽永成电子机械技术有限公司| 布勒机械设备有限公司| 贵州工程机械有限公司| 沈阳瑞熠机械有限公司| 昆山尚亦精密机械有限公司| 上海拓稳机械有限公司| 唐山粤丰钢铁有限公司| 中山市包装机械有限公司| 山东重工机械有限公司| 新乡市西贝机械有限公司| 山东长城起重机械有限公司| 河南昌申钢铁有限公司| 南通奥普机械工程有限公司 | 广东佛山机械有限公司| 河北小松工程机械贸易有限公司 | 江苏飞耀机械制造有限公司| 粮油机械设备有限公司| 安丘博阳机械制造有限公司| 青岛精密机械有限公司| 威海祥光机械有限公司| 德龙钢铁有限公司地址| 锋机械设备有限公司| 无锡科创机械设计制造有限公司| 济南快克数控机械有限公司 | 广西玉柴动力机械有限公司| 宁波佳尔灵气动机械有限公司 | 天津同盈钢铁有限公司| 山东威达机械有限公司| 海狮洗涤机械有限公司| 石嘴山钢铁有限公司| 翼虎动力机械有限公司| 马长江钢铁有限公司| 邢台钢铁有限公司官网| 台州欧玮机械有限公司| 郑州水工机械有限公司| 临海市机械有限公司| 辽阳新达钢铁有限公司| 苏州昶智精密机械有限公司| 郑州食品机械有限公司| 溧阳三元钢铁有限公司| 浙江中禾机械有限公司| 苏州精雕精密机械工程有限公司| 迪威玻璃机械有限公司| 安印刷机械有限公司| 新乡市特昌振动机械有限公司| 山东海诺机械有限公司| 上海传动机械有限公司| 重庆蓝黛动力传动机械有限公司| 广东富华重工制造有限公司| 济南市恒宇机械有限公司| 环保机械设备有限公司| 翰林机械制造有限公司| 海星机械制造有限公司| 昌乐 机械 有限公司| 杭州驰林机械有限公司| 东莞市机械设备有限公司| 上海开隆冶金机械制造有限公司 | 南通凯瑞德机械有限公司| 化工机械制造有限公司| 佛山市松川包装机械有限公司| 常州凯发动力机械有限公司| 芜湖 机械有限公司| 华通动力重工有限公司| 金华机械 有限公司| 昆山裕邦机械有限公司| 常州工程机械有限公司| 武汉千里马工程机械有限公司| 深圳精密机械有限公司| 营口京华钢铁有限公司招聘| 郑州郑瑞机械有限公司| 张家港市贝尔机械有限公司| 溧阳机械制造有限公司| 湖北天和机械有限公司| 沈阳凯力拓机械设备有限公司| 宁波利豪机械有限公司| 江阴市祥达机械制造有限公司| 山西万泽锦达机械制造有限公司| 江苏华光双顺机械制造有限公司 | 东莞市康机械有限公司| 阿特拉斯工程机械有限公司| 苏州博机械有限公司| 浙江建达机械有限公司| 起帆电缆有限公司上市| 徐州东亚钢铁有限公司| 青岛永正化工机械有限公司| 智能机械设备有限公司| 山东永峰钢铁有限公司| 挤出机械 有限公司| 台山市机械厂有限公司| 湖南龙凤机械制造有限公司| 深圳市奥德机械有限公司| 东莞市通盛机械有限公司| 东莞市从创机械有限公司| 温州工程机械有限公司| 佛山市创利宝包装机械有限公司| 嘉兴 精密机械有限公司| 徐州凯工机械有限公司| 上海德珂斯机械自动化技术有限公司| 苏州起重机械有限公司| 河南矿山机械有限公司| 威海欧东机械有限公司| 青岛美光机械有限公司| 人和弹簧机械有限公司| 江苏天泽精工机械有限公司| 广东粤韶钢铁有限公司| 常州博成机械有限公司| 广州山推机械有限公司| 唐山松汀钢铁有限公司| 四川望锦机械有限公司| 上海优拜机械有限公司| 佛山市万为包装机械有限公司| 佛山市松川机械设备有限公司| 山东起重机有限公司| 上海鑫越包装机械有限公司| 农友机械设备有限公司| 阿尔法起重机有限公司| 山西机械设备有限公司| 宜兴富曦机械有限公司| 无锡科创机械设计制造有限公司| 上海好机械有限公司| 湖北仙粮机械有限公司| 天津市天重江天重工有限公司| 济南液压机械有限公司| 河北中浩机械制造有限公司| 卡麦龙机械有限公司| 合肥至信机械有限公司| 宣城市建林机械有限公司| 上海传动机械有限公司| 宿迁机械制造有限公司| 山东泰瑞汽车机械电器有限公司 | 南通武藏精密机械有限公司招聘| 湖南华菱湘潭钢铁有限公司| 诸城市安泰机械有限公司| 苏州盈合机械有限公司| 无锡盛达机械制造有限公司| 河南江河机械有限公司| 湖北江重机械制造有限公司| 昆山市众捷塑料机械有限公司| 徐州 机械有限公司| 杭州 尔机械有限公司| 青岛液压机械有限公司 | 山推楚天工程机械有限公司| 深圳龙润彩印机械设备有限公司| 浙江歌德起重机有限公司| 中阳钢铁有限公司官网| 沈阳奎鑫钢铁有限公司| 成都的起重有限公司| 济南包装机械械有限公司| 鸿源机械制造有限公司| 上海鼎龙机械有限公司| 北京机械制造有限公司| 泰安鑫杰机械有限公司| 上海臣轩机械有限公司| 东莞麒麟机械有限公司| 山东起重机械有限公司| 苏州辽鞍机械有限公司| 山东重特机械有限公司| 杭州泰尚机械有限公司| 上海臣轩机械有限公司| 浙江荣升机械有限公司| 化工有限公司起名大全| 青岛塑料机械有限公司| 山东米科思机械设备有限公司 | 江苏鼎盛重工有限公司| 斗山工程机械有限公司| 郑州华隆机械制造有限公司| 天津动力机械有限公司| 东莞液压机械有限公司| 安徽食品机械有限公司| 台在机械设备有限公司| 常州市菲德机械部件有限公司| 四川瑞迪佳源机械有限公司 | 宿迁百通机械有限公司| 章丘市宇龙机械有限公司| 常州铁本钢铁有限公司| 滕州三合机械有限公司| 重庆力劲机械有限公司| 天津金岸重工有限公司| 江苏金鹰流体机械有限公司 | 道依茨法尔机械有限公司| 上海石油机械有限公司| 芜湖 机械 有限公司| 新乡市中天机械有限公司| 四川久进机械制造有限公司 | 青岛三益塑料机械有限公司| 北京机械设备有限公司| 柳工常州机械有限公司| 镇江机械制造有限公司| 重庆宝汇跨搏机械制造有限公司| 南京恩梯恩精密机械有限公司| 山东信川机械有限公司| 无锡通用机械厂有限公司| 华宇机械制造有限公司| 鞍山宝得钢铁有限公司| 重庆旺田机械有限公司| 苏州雁达机械有限公司| 兰州兰石重工有限公司| 上海松井机械有限公司| 河北卓昊机械制造有限公司| 福州优利机械有限公司| 广州华劲机械有限公司| 浙江炜冈机械有限公司| 星包装机械有限公司| 哈克农业机械装备制造有限公司| 三木机械制造实业有限公司| 龙口金正机械有限公司| 山西新泰钢铁有限公司| 台州市鲨鱼食品机械有限公司| 江苏八达重工机械有限公司| 宁波华热机械制造有限公司 | 厦门工程机械有限公司| 洛阳泽华机械设备有限公司| 泉州金鹰机械有限公司| 昆山万利机械有限公司| 安丘机械制造有限公司| 巩义市瑞赛克机械设备有限公司| 机械设备有限公司经营范围| 上海申克机械有限公司| 佛山市南海鼎工包装机械有限公司| 湖北川谷机械有限公司| 华盛机械设备有限公司| 比富机械(东莞)有限公司| 东莞市嘉鲁特注塑机械有限公司| 江苏宇达机械有限公司| 沈阳三重机械有限公司| 昆山乙盛机械工业有限公司电话 | 潍坊润鑫机械有限公司| 许昌机械制造有限公司| 杭州灵达机械有限公司| 北京航天振邦精密机械有限公司| 日照机械制造有限公司| 华亿机械制造有限公司| 滁州富达机械电子有限公司| 新乡市豫新起重机械有限公司 | 常州市工程机械有限公司| 北仑旭升机械有限公司| 沈阳祺盛机械有限公司| 常州市 机械设备有限公司| 新昌县蓝翔机械有限公司| 湖北银轮机械有限公司| 成都欧曼机械有限公司| 无锡祥靖机械有限公司| 沁阳宏达钢铁有限公司| 温州朝隆纺织机械有限公司| 昆山圣源机械有限公司| 焦作 机械 有限公司| 泰上机械设备有限公司| 郑州包装机械有限公司| 友池精密机械有限公司| 山东永健机械有限公司| 广州恒联食品机械有限公司| 浙江胜代机械有限公司| 济南业兴通工程机械有限公司| 上海伍行机械设备有限公司| 湖南力诺机械有限公司| 上海鑫水机械有限公司| 溧阳三元钢铁有限公司| 杭州鸿机械有限公司| 洛阳高峰工程机械有限公司| 大连船舶重工有限公司| 沈阳鸿本机械有限公司| 郑州市长城重工机械有限公司| 招远华丰机械设备有限公司 | 青岛西城铸造机械有限公司| 东莞启益电器机械有限公司| 江苏宏达起重电机有限公司| 苏州金纬机械制造有限公司| 物理农林机械有限公司| 苏州动力机械有限公司| 高臻机械设备有限公司| 济南恒铭钢铁有限公司| 夹江水工机械有限公司| 青岛浩翔机械有限公司| 济南钢铁 有限公司| 临沂江鑫钢铁有限公司| 德国arku机械制造有限公司| 吴江机械设备有限公司| 广西清隆机械制造有限公司| 新乡市欧霖佳机械有限公司| 华群数控机械有限公司| 重庆蓝黛动力传动机械有限公司| 扬州液压机械有限公司| 农业发展有限公司起名| 河北强华水利机械有限公司| 珠海市机械设备有限公司| 兰溪永丰机械有限公司| 沈阳联合利邦机械有限公司| 广州赛思达机械设备有限公司 | 苏州精创机械有限公司| 扬州三源机械有限公司| 杭州金鸥机械有限公司| 常州市 机械设备有限公司| 苏州腾龙机械有限公司| 河北坤达起重设备有限公司| 昆成机械昆山有限公司| 烨隆精密机械有限公司| 合肥逸飞包装机械有限公司| 山东领品机械有限公司| 新疆八一钢铁有限公司| 湖州卓信机械有限公司| 沧州沧狮磨浆机械有限公司| 临沂工程机械有限公司| 乙盛机械工业有限公司| 意达纺织机械有限公司| 滦南华瑞钢铁有限公司| 河南卫华起重机有限公司| 厦门洪海机械有限公司| 艾沃意特机械设备制造有限公司 | 范斯特机械有限公司| 郑州东方尚武食品机械有限公司| 青岛迪恩机械制造有限公司| 无锡橡塑机械有限公司| 河北九江钢铁有限公司| 郑州市天赐重工机械有限公司| 常州市佳凯包装机械有限公司| 上海轻工机械有限公司| 成都固特机械有限公司| 河南大方起重机有限公司| 上海永策机械设备有限公司 | 沧州机械制造有限公司| 山东山建机械有限公司| 中泰机械设备有限公司| 浙江中意机械有限公司| 东莞宝科机械有限公司| 浙江天风塑料机械有限公司| 哈尔滨恒力达机械有限公司| 江苏苏盐阀门机械有限公司| 张家港长力机械有限公司| 泰安煤矿机械有限公司| 无锡大力起重机械有限公司| 济南闽源钢铁有限公司| 大连东拓工程机械制造有限公司 | 上海伍行机械设备有限公司| 渡边食品机械有限公司| 无锡锡南铸造机械有限公司| 山东川普机械有限公司| 常州万裕机械有限公司| 江苏双友重型机械有限公司| 上海传动机械有限公司| 资阳 机械有限公司| 宁波食品机械有限公司| 浙江卓驰机械有限公司| 徐州徐工施维英机械有限公司| 江西机械设备有限公司| 永明机械制造有限公司| 山东工程机械有限公司| 太行机械工业有限公司| 肥城金塔机械有限公司| 永红铸造机械有限公司| 山东康弘机械有限公司| 潍坊凯信机械有限公司| 莱州行星机械有限公司| 永红铸造机械有限公司| 华夏机械设备有限公司| 浙江云广机械制造有限公司| 日照立盈机械有限公司| 青岛鲁耕农业机械有限公司| 湖南天拓重工机械有限公司| 瑞迪机械实业有限公司|